
Laboratory Measurement Of Body Composition
Body composition refers to the relative percentages of body weight comprised of fat and fat free body tissue. It is used in the assessment of nutritional and growth status and in disease states and their treatment. Weight is an overall measure of your body mass. At any rate these 9 indicators are some of the most important factors to consider. Assessment techniques vary from simple field measurements to elaborate laboratory techniques that require expensive equipment and specially trained technicians. Common methods for body composition assessment include hydrostatic.
A quick google search will reveal a number of different ways to measure body mass and composition. Our laboratory utilizes 2 devices for this measurement. The simplest approach in body composition is the 2c model dividing body weight into fat mass fm and fat free mass ffm. The purpose of the body composition laboratory is to conduct research in the area of body composition and carry out measurements of body composition and energy expenditure to monitor growth nutritional status rehabilitation and energy requirements in a variety of clinical conditions. These high precision measurements are associated with body water mineral protein and fat content. The measurement of body composition occurs in many branches of biology and medicine.
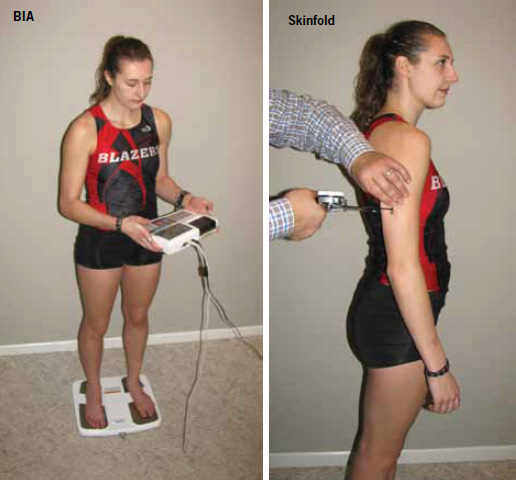
Impedimed sfb7 and the inbody 720. The cnrc body composition laboratory is the only laboratory of its type in the nation that can provide a complete complement of body composition measurements in all populations ranging from low birth weight infants to adults. Ongoing efforts involve multisegmental and multifrequency bioelectrical impedance analysis quantitative magnetic resonance for total body water fat and lean tissue measurements imaging to further define ectopic fat depots. A multi frequency unit bis. Energy stores skeletal muscle and protein content can be determined and changes monitored. Body composition can be estimated by measuring total body water.
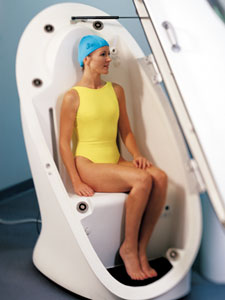
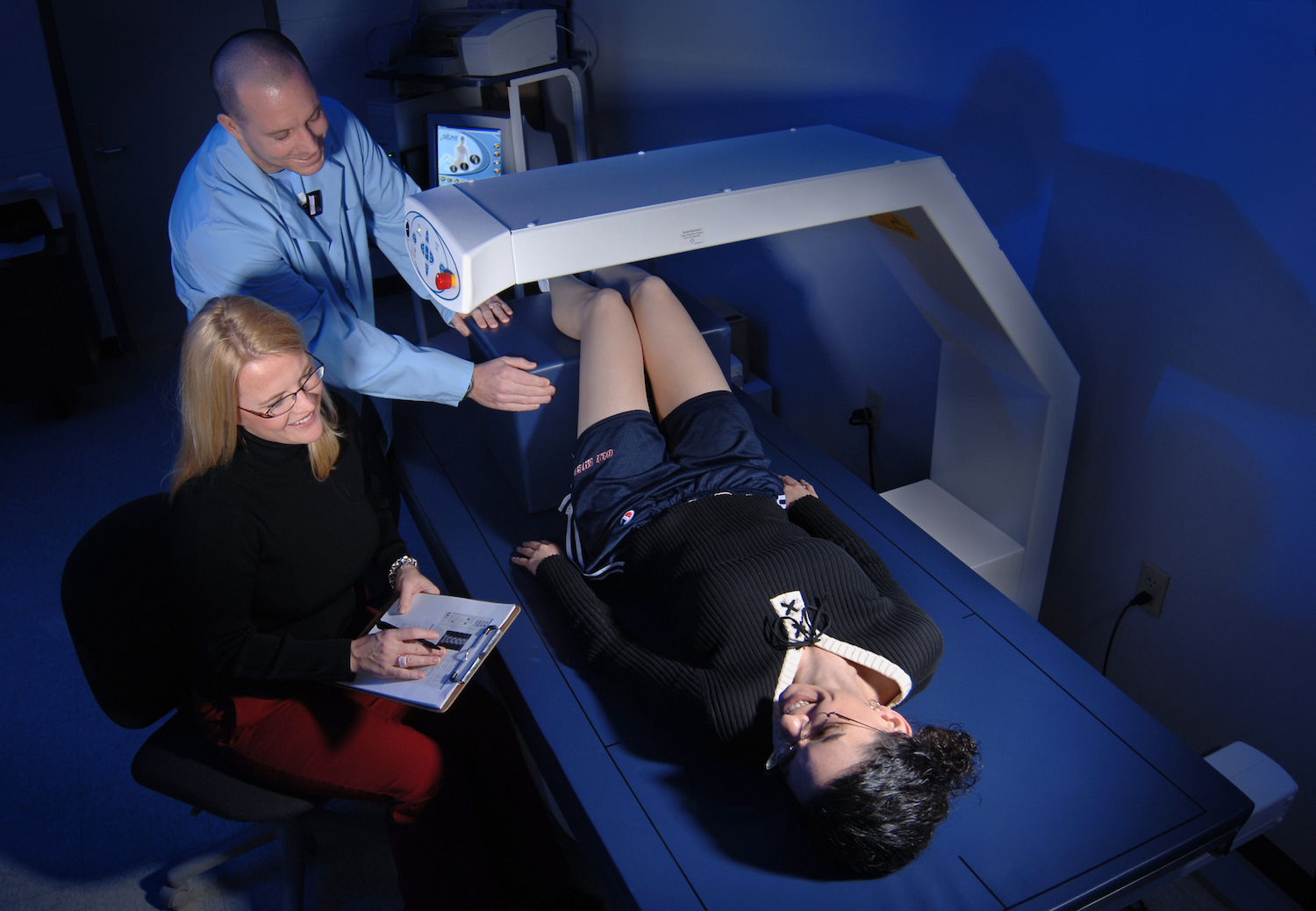
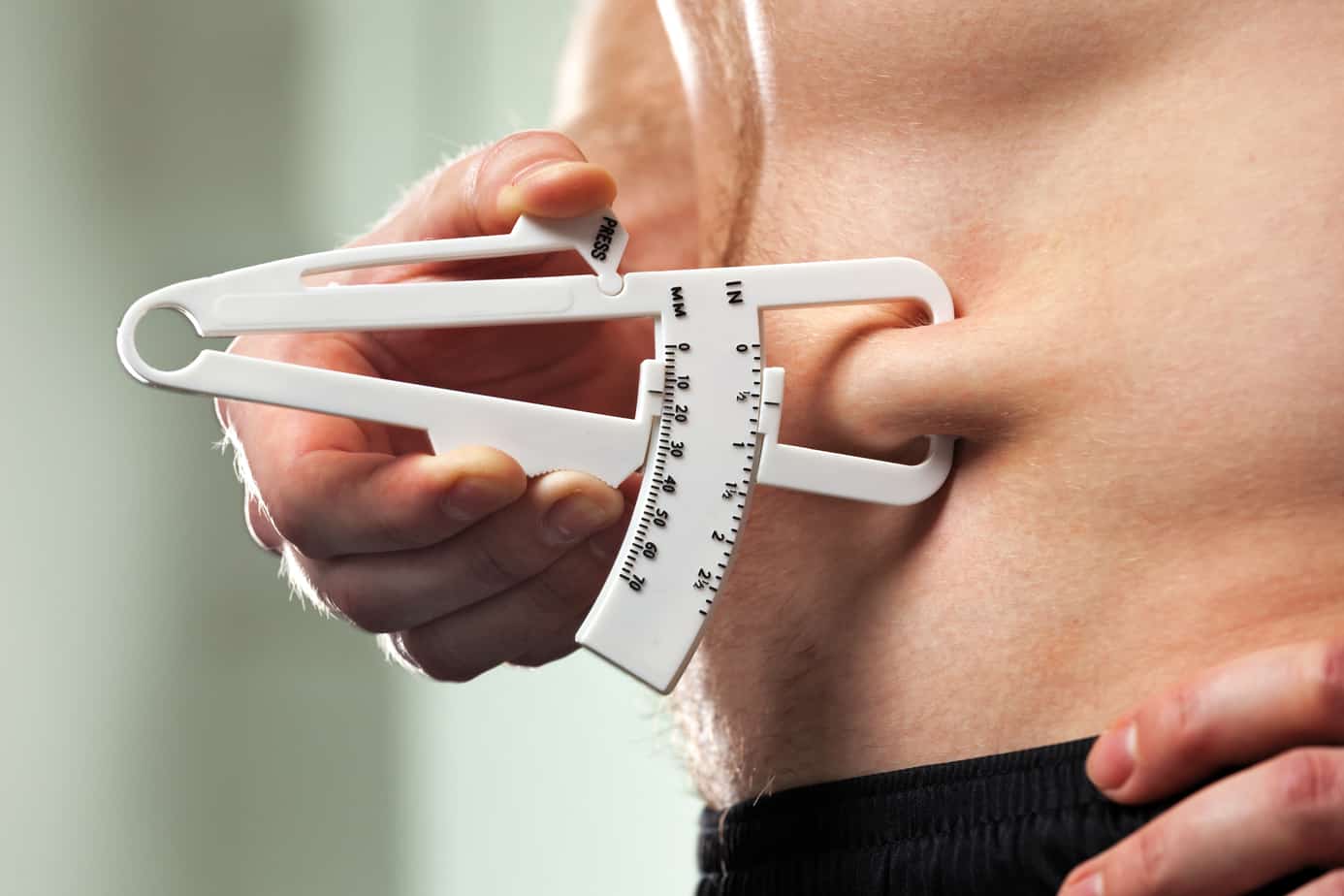
Body composition measurement methods are continuously being perfected. Laboratory measurements of body composition densitometry the application of densitometry to the measurement of human body composition is based on the principle that if thebodyisregardedasbeingmadeupoftwocomponents ofknowndensitiesthenthebodydensityisdeterminedby the relative proportions of the two components. There is a multitude of established methods and techniques for in vivo estimation of body composition ranging from simple field methods for example skinfold measurement to laboratory methods such as dual energy x ray absorptiometry dxa hydrostatic weighing and the more complex in vivo neutron acti vation analysis. The anhydrous fm is the chemically extractable fat with an assumed density of 09007 gcm3 whereas the ffm is assumed to have a density of 11000 gcm3and water content of 7372 per cent7. These devices provide details of intra and extracellular fluid as well as fat mass fat free mass and percent body fat. This measurement includes all of the elements of your body bones blood organs muscles and fat.
Random Post
- best app for body measurement
- maanvi gagroo body measurement
- visual of body measurements
- meryl streep body measurement
- body measurements in tamil
- evan rachel wood body measurement
- joy taylor body measurement
- lindsay lohan body measurement
- arunima hazra body measurement
- chris pratt body measurement
- sanya lopez body measurement
- taking body measurement for polo shirt
- body measurement thighs
- radhika pandit body measurement
- nivin pauly body measurement
- sabnam faria body measurement
- body measurements equations
- m and s bra measurement
- vehicle body measurement
- aaliyah body measurement
- bra size quora
- bhagyashree body measurement
- bebe rexha body measurement
- body measurement hair type
- sana fakhar body measurement
- saundarya body measurement
- ideal male body measurements
- body measurement jml
- anand arnold body measurement
- amrapali dubey body measurement
- bra sizes with picture
- thandie newton body measurement
- bts jimin body measurement
- nisha dubey body measurement
- ashnoor kaur body measurement
- chloe bailey body measurement
- mahima makwana body measurement
- fish body length measurement
- body measurement cctv
- lee min ho body measurement
- uk body measurement chart
- saira banu body measurements
- body measurement app tracker
- ideal body measurement ratios
- youtube body measurements
- your body measurement
- bra fitting questions
- nicola peltz body measurement
- plus size body measurements
- body measurement diagram


























/GettyImages-180403783-59036e885f9b5810dc0611b2.jpg)






