Body Fluid Compartments And Their Measurement
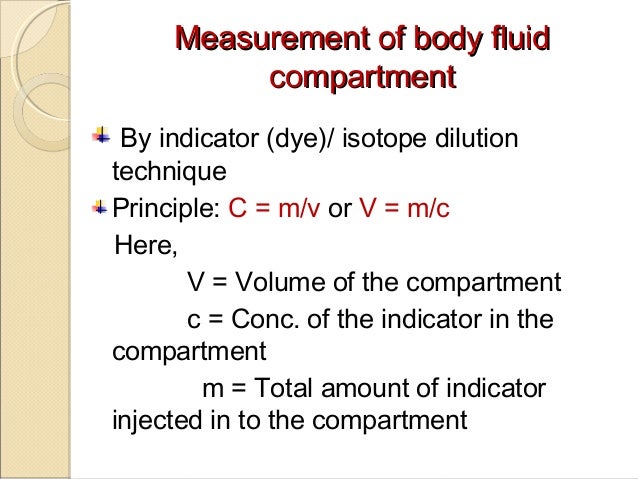
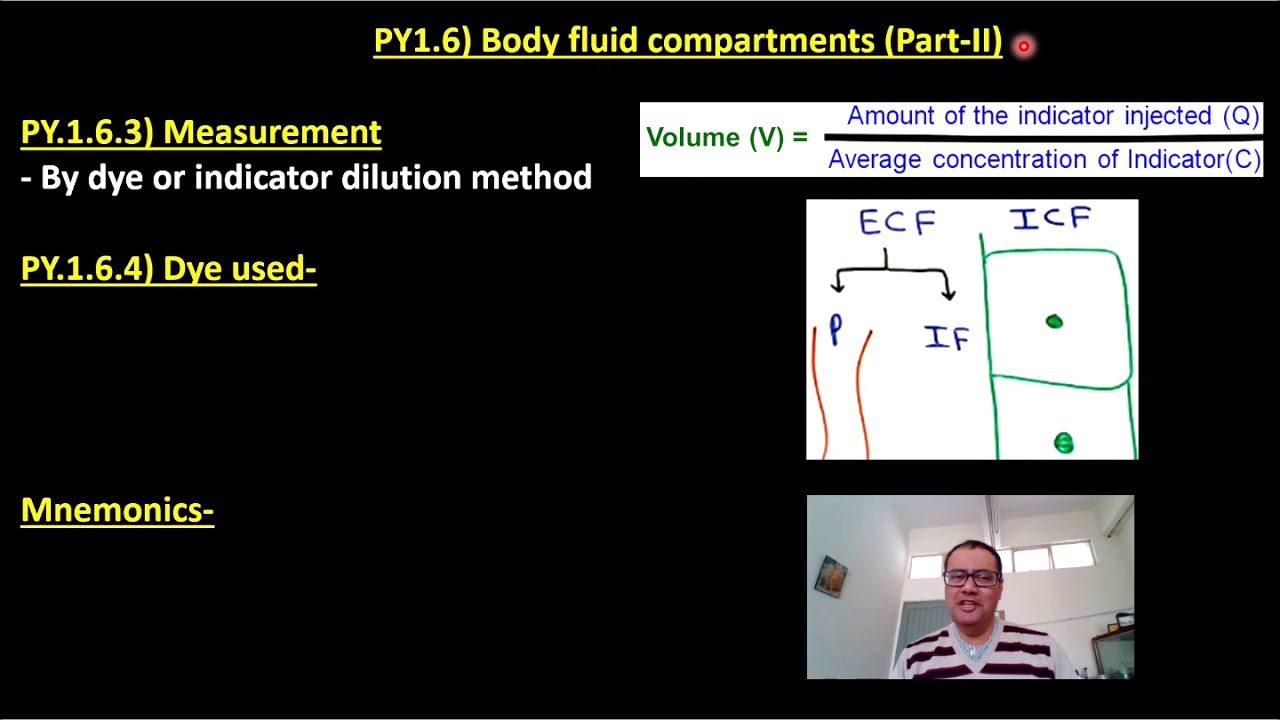
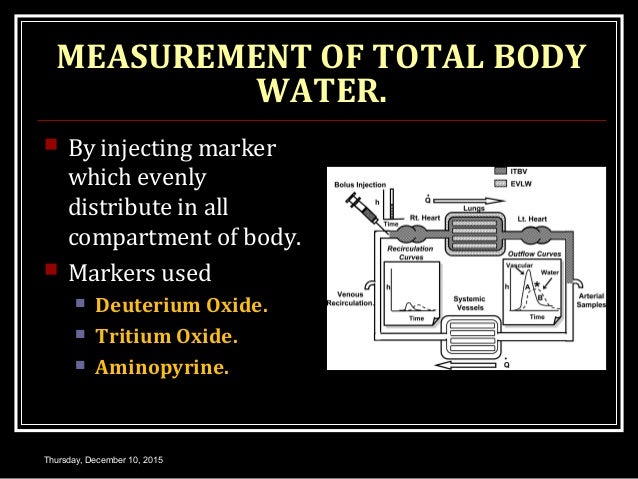
If the amount of the substance is known and the resulting concentration is measured the volume can be calculated. Body fluid compartments can be measured by dilution of a compound that distributes only in the space of interest. Extracellular fluid compartment further. Indicator dilution method depends upon law of conservation of mass. This is a simplified arabic illustration for the medical students if you have any questions please dont hesitate to contact me at fb. Measurement of different body fluid compartments.
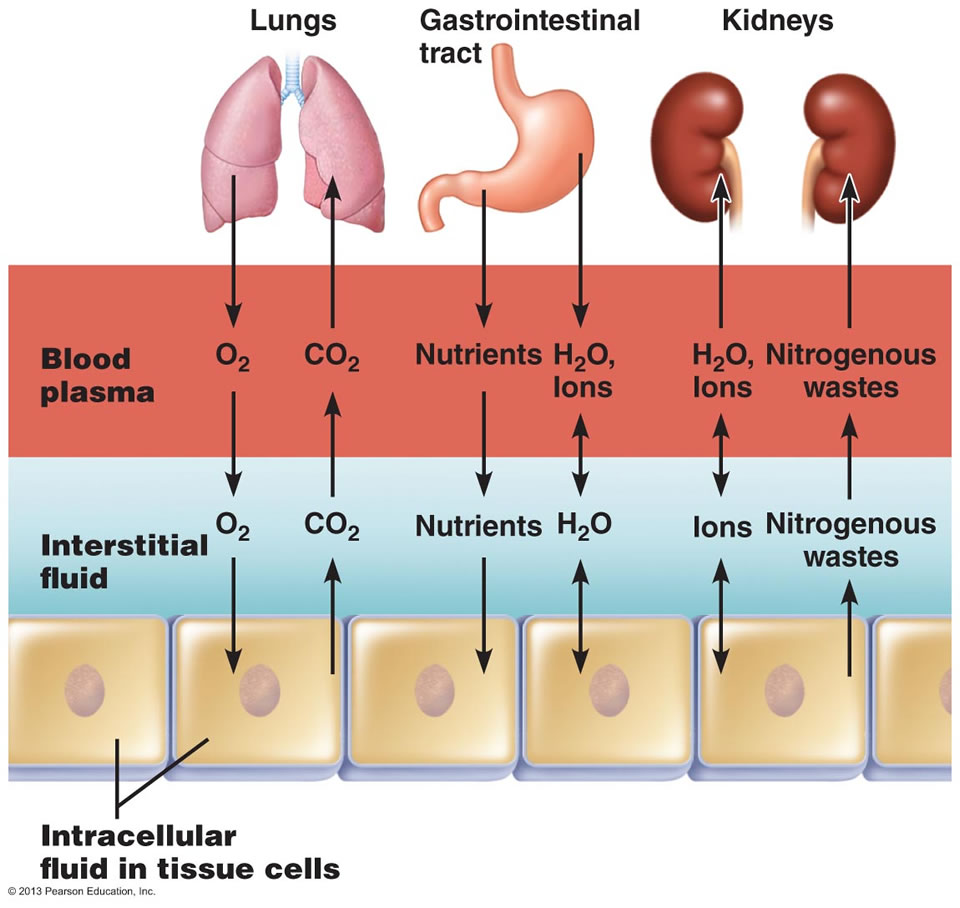
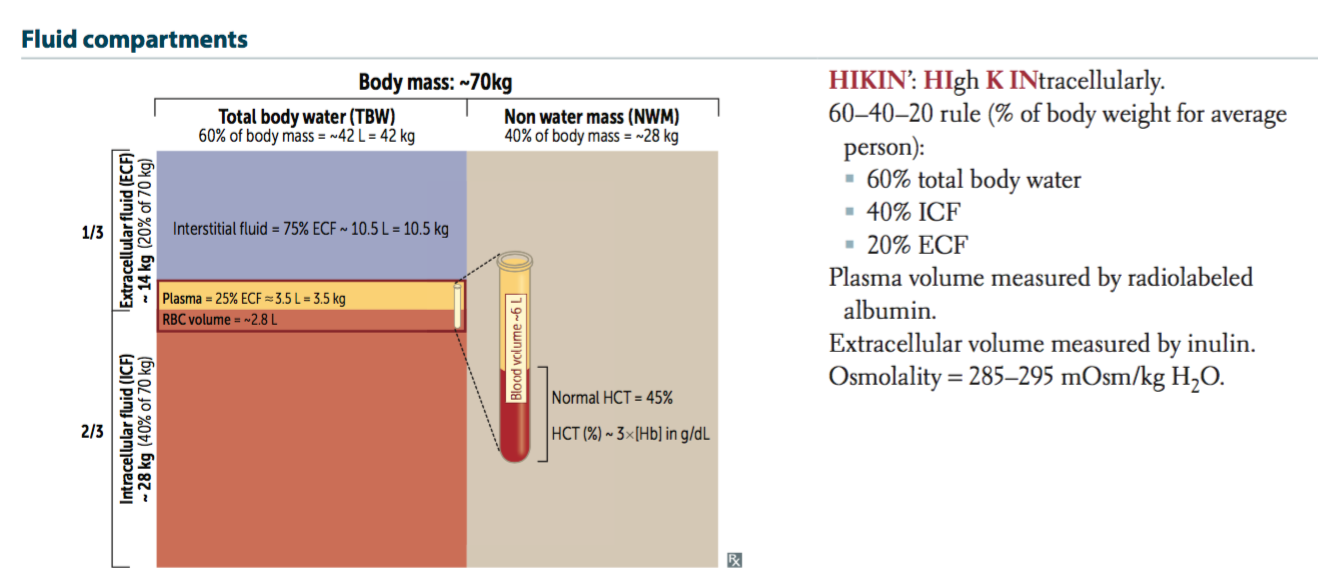
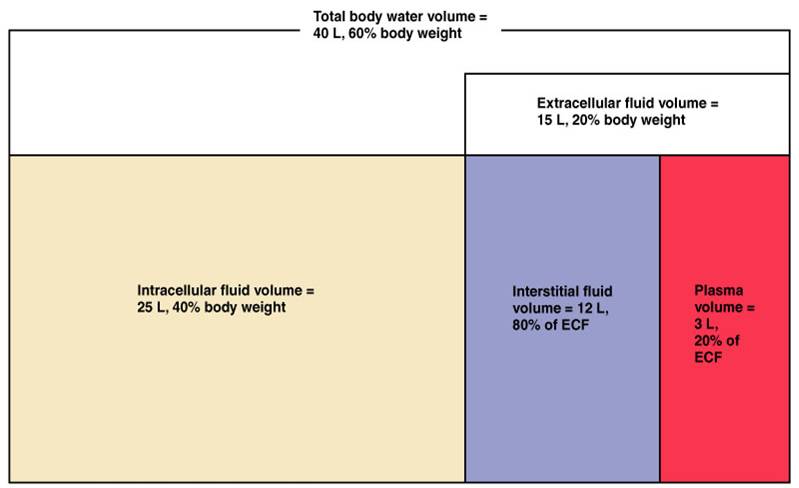
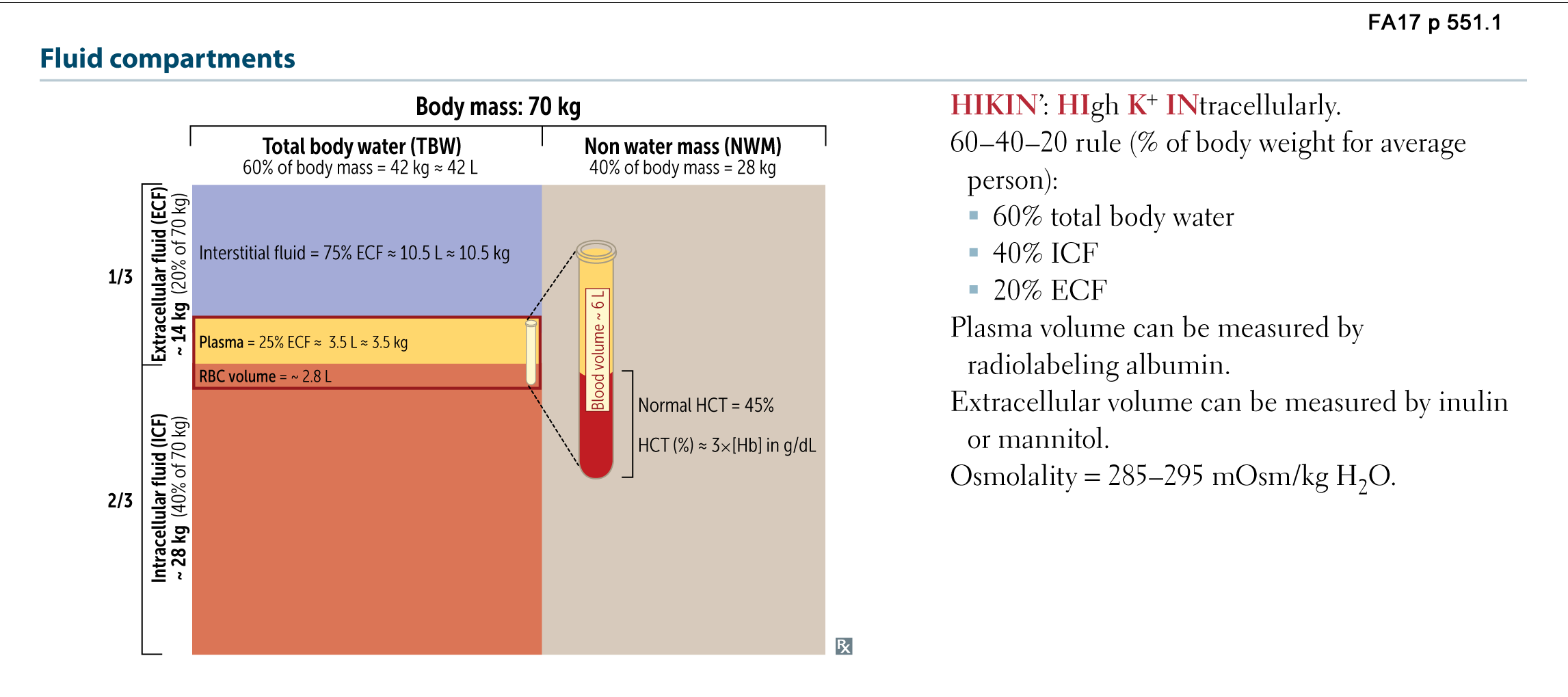
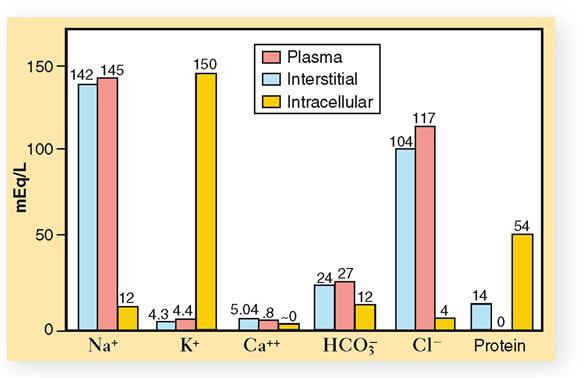
These include intracellular fluid and extracellular fluid. About two thirds is in the intracellular fluid compartment icf. Body fluids can be discussed in terms of their specific fluid compartment a location that is largely separate from another compartment by some form of a physical barrier. The intracellular fluid icf compartment is the system that includes all fluid enclosed in cells by their plasma membranes. The total body water is divided into compartments and useful physiological insight and some measure of clinical predictability can be gained from this approach even though most of these fluid compartments do not exist as discrete real fluid collections. There are two main fluid compartments water occupies in the body.
Fluid compartments are defined by their position relative to the cellular membrane of the cells that make up the bodys tissues. Intracellular fluid the intracellular fluid of the cytosol or intracellular fluid or cytoplasm is the fluid found inside cells. The indicator dilution principle is based on the definition of a concentration. So the more muscles one has the higher the total body water will be. Total body water is 60 of body weight and is divided into various body fluid compartments. Total mass of the indicator after distribution in the compartment is the same as the mass before distribution.
The intracellular fluid is the fluid within the cells of the body. The intracellular fluid icf compartment is the system that includes all fluid enclosed in cells by their plasma membranes. The two main fluid compartments are the intracellular and extracellular compartments. The human body and even its individual body fluids may be conceptually divided into various fluid compartments which although not literally anatomic compartments do represent a real division in terms of how portions of the bodys water solutes and suspended elements are segregated. Body fluids can be discussed in terms of their specific fluid compartment a location that is largely separate from another compartment by some form of a physical barrier. Indicator properties disperses evenly throughout the compartment.
In contrast skeletal muscle contains 75 water.
Random Post
- bra size eu to us
- pug body measurement
- the criterion measurement of body composition
- mahira sharma body measurement
- body measurement equipment
- naira body measurements
- female body measurement guide
- poonam jhawer body measurement
- marks and spencer bra measurement service
- body temperature measurement en español
- body measurements water
- bra fitting yours
- meena body measurements
- bra fitting jamaica
- body measurement calculator female
- zhc body measurement
- body measurement catherine zeta jones
- wamiqa gabbi body measurement
- body bag measurements
- ideal body measurements by height
- sana saeed body measurement
- nicole wallace body measurement
- karthika muralidharan body measurements
- geraldine viswanathan body measurement
- calculate bmi using body measurements
- nfl player body measurements
- judy greer body measurement
- body temperature measurement lazada
- body measurements in hindi
- abel albonetti body measurement
- body measurement eva green
- mashal khan body measurement
- ideal body measurement for female
- alicia schmidt body measurement
- kpop idol body measurements
- measurement of body weight length and circumference
- body frame size measurement
- ridhima pandit body measurement
- twice dahyun body measurement
- sabrina carpenter body measurement
- darshan raval body measurement
- soom super gem body measurements
- girth measurement body composition
- advantages and disadvantages of body measurement
- xbox body measurement
- body measurements blouse cutting and stitching
- bilal abbas body measurement
- plus size bra measurement calculator
- rene russo body measurement
- hayley atwell body measurement